Indication and Usage
MOZOBIL® (plerixafor) injection is indicated in combination with filgrastim to mobilize hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) to the peripheral blood for collection and subsequent autologous transplantation in patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) or multiple myeloma (MM).
Mozobil + Filgrastim Decreased the Number of Apheresis Days Compared With Filgrastim Alone2
Study Design
Two phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies evaluated the efficacy and safety of Mozobil (0.24 mg/kg) + filgrastim (10mcg/kg) vs placebo + filgrastim (10mcg/kg) in patients with MM (N=302) or NHL (N=298)2-4
Primary End Point

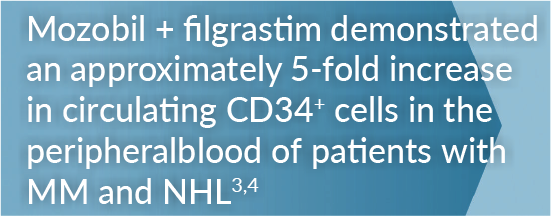
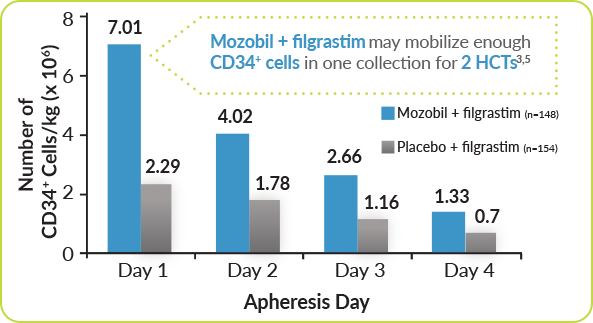
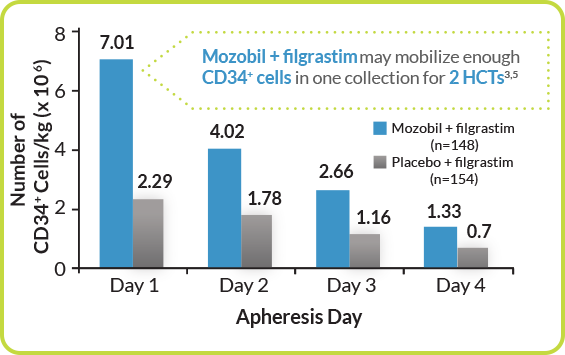
Mozobil + Filgrastim Helped Achieve Greater Day One Collection for Patients With MM3
Mozobil + Filgrastim Demonstrated a >3-Fold Greater Day One Collection Compared With filgrastim Alone3
Secondary End Point
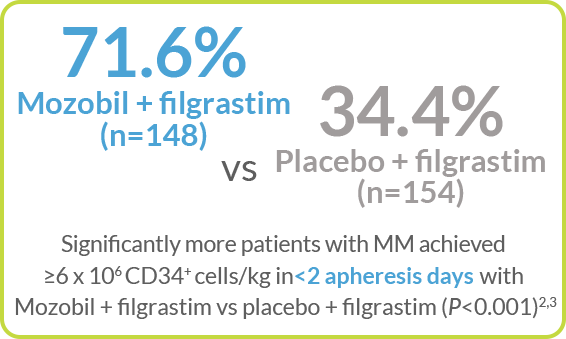
Kaplan-Meier Estimate of the Proportion of Patients With MM Who Achieved ≥6 x 106 CD34+ cells/kg, by Apheresis Day3
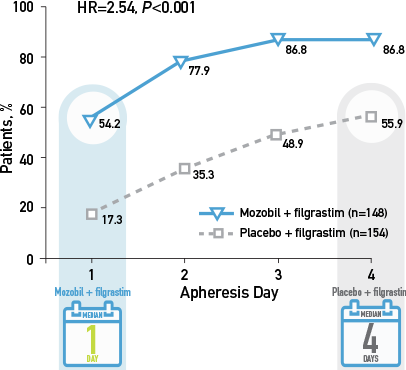
>50% of patients with MM achieved ≥6 x 106 CD34+ cells/kg in 1 day with Mozobil + filgrastim vs 4 days with filgrastim alone2
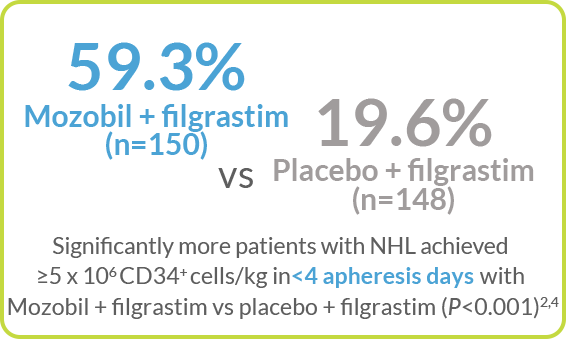
Kaplan-Meier Estimate of the Proportion of Patients With NHL Who Achieved ≥5 x 106 CD34+ cells/kg, by Apheresis Day4
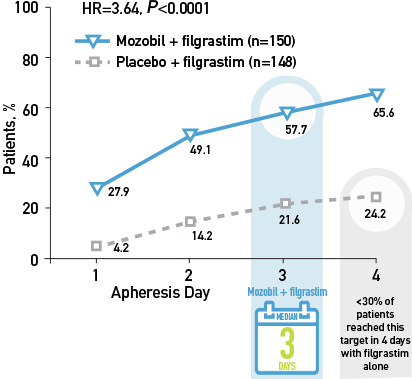
>50% of patients with NHL achieved ≥5 x 106 CD34+ cells/kg in 3 days with Mozobil + Filgrastim vs <30% reaching the collection target in 4 days with filgrastim alone2
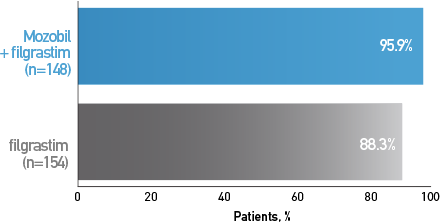
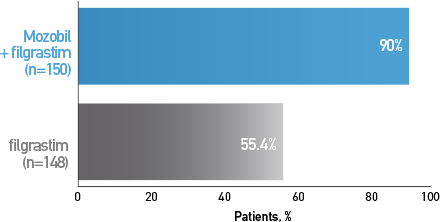
Mozobil + Filgrastim Allowed More Patients to Proceed to HCT3,4
Secondary End Point: Post Hoc Analysis*
Percentage of Patients With MM Who Proceeded to HDT/HCT Based on Their Mobilization Regimen3
Percentage of Patients With NHL Who Proceeded to HDT/HCT Based on Their Mobilization Regimen4
*Patients with MM or NHL receiving Mozobil + Filgrastim vs patients receiving filgrastim alone, who underwent transplant based on achievement of a minimum number of collected cells.3,4
- Multiple factors can influence time to engraftment and graft durability following HCT2
- For transplanted patients in the Phase 3 studies, time to neutrophil and platelet engraftment and graft durability were similar across the treatment groups2
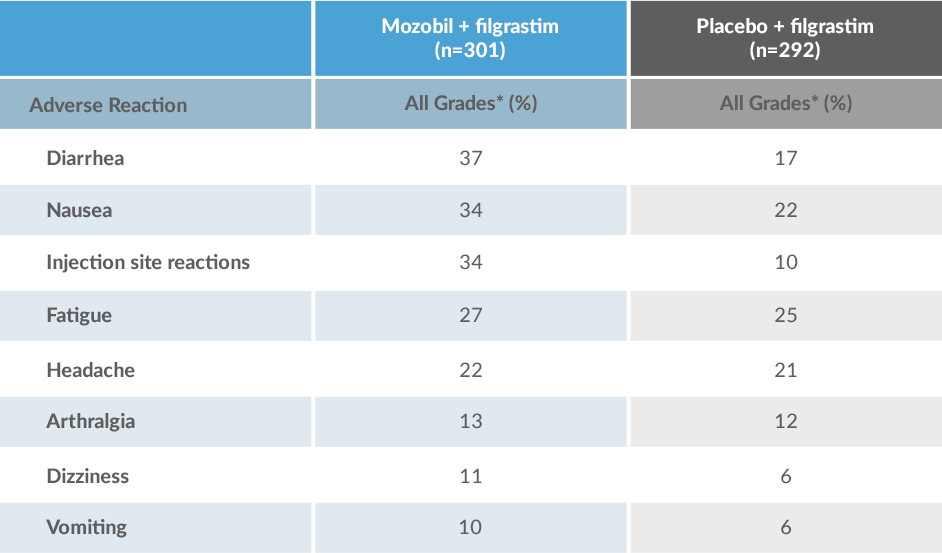
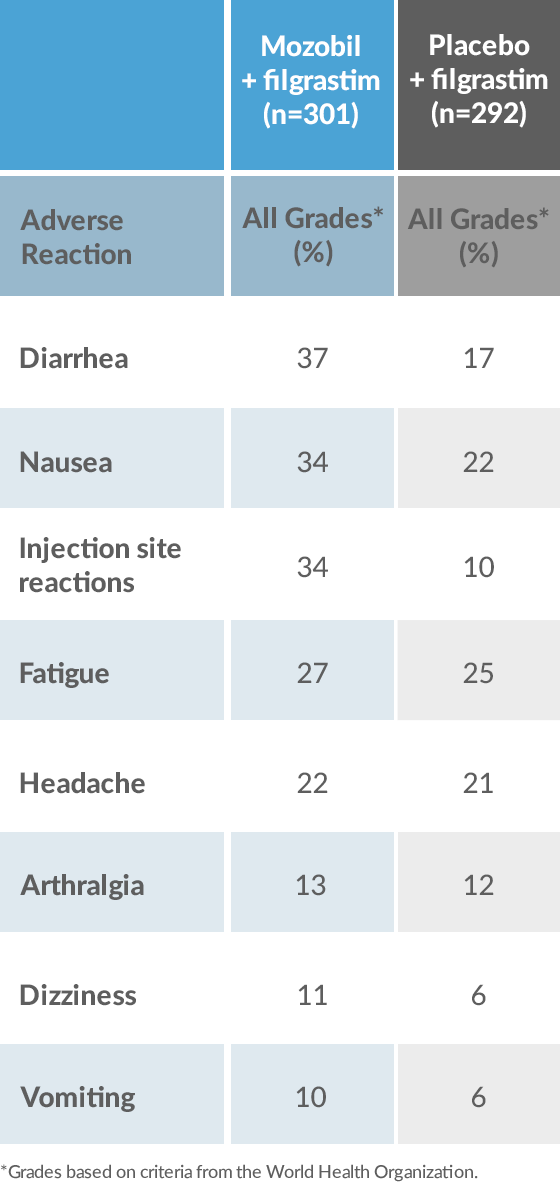
Mozobil + Filgrastim Has an Established Safety Profile2-4

Adverse Reactions in ≥10% of Patients With NHL and MM Receiving Mozobil + Filgrastim or Placebo + filgrastim During HSC Mobilization and Apheresis2
*Grades based on criteria from the World Health Organization.
Mozobil Reversibly Blocks the CXCR4/SDF-1α Interaction2
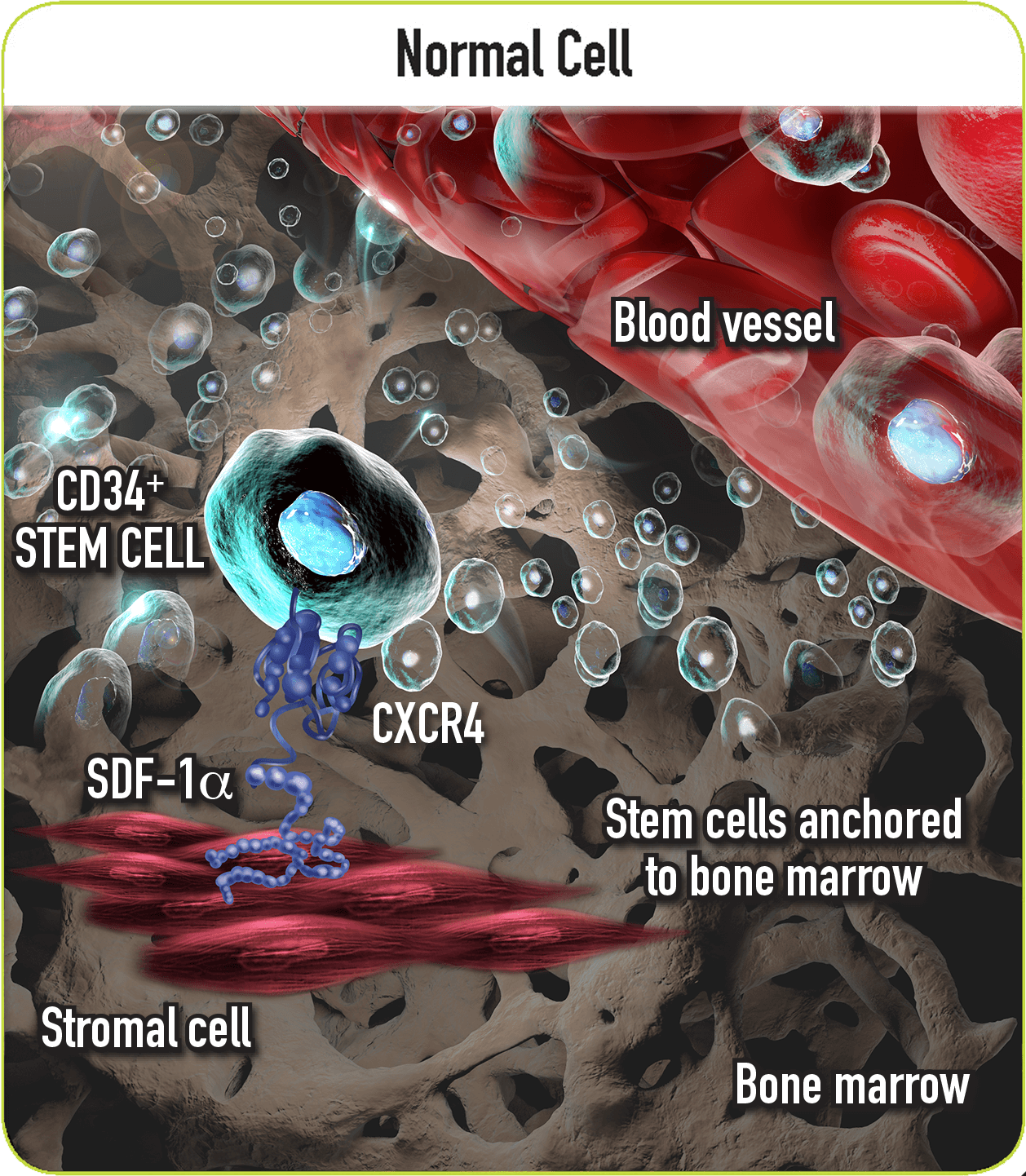
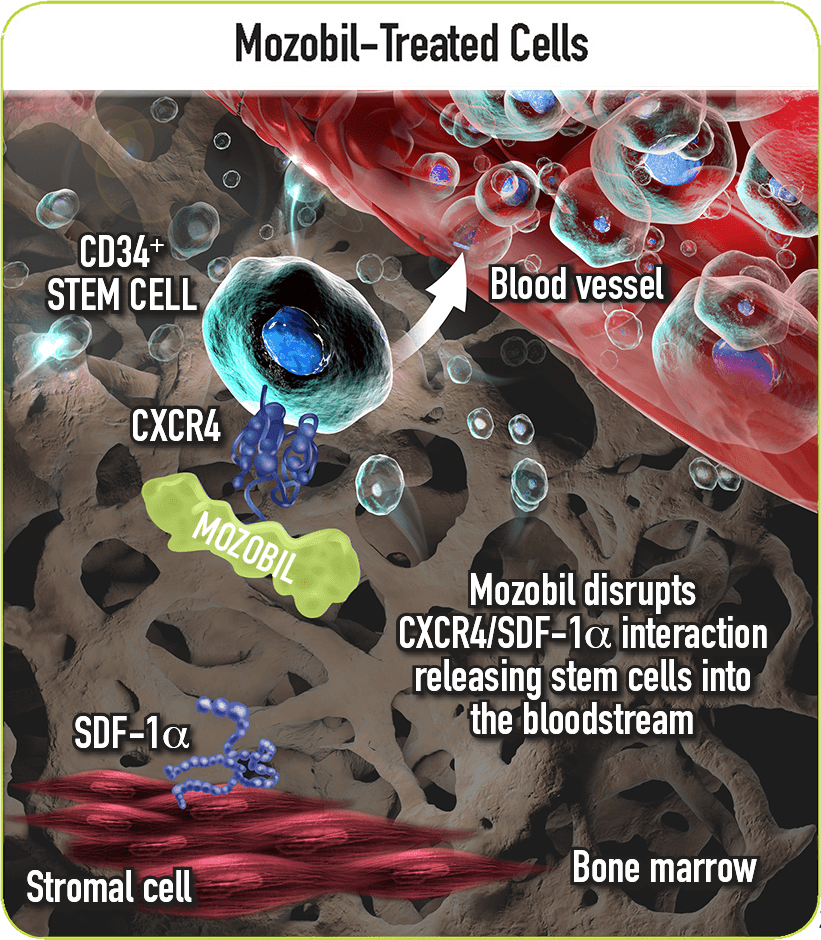
- Once in the marrow, stem cell CXCR4 can act to help anchor these cells to the marrow matrix, either directly via SDF-1α or through the induction of other adhesion molecules2
- As an inhibitor of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor, Mozobil reversibly blocks binding of its cognate ligand, SDF-1α2
- This action allows the release of stem cells from the bone marrow into the circulating blood2